Diagnosis: Rosacea
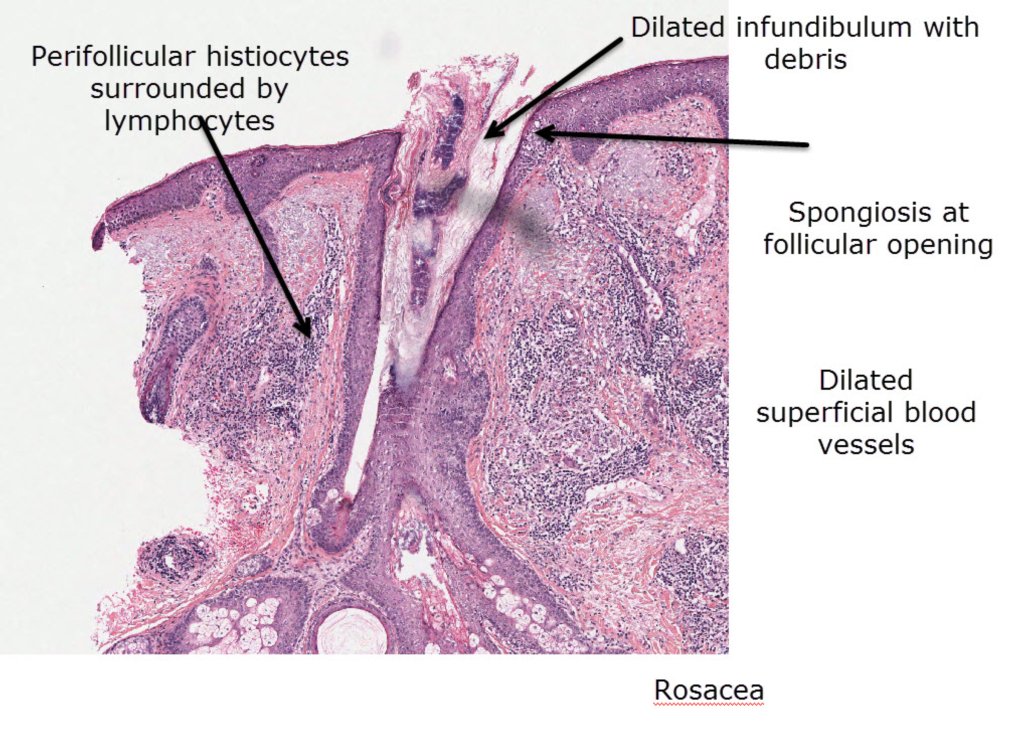
Description: Here the major features are dilated infundibulum with some plugging, focal parakeratosis, focal spongiosis at the follicular opening plus a perifollicular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Many of the dermal blood vessels are dilated
Clinical Features: Papules,red
Pathology/Site Features: Face
Sex: F
Age: 35
Submitted By: Ian McColl
Differential DiagnosisHistory:
Rosacea Here the major features are dilated infundibulum with some plugging, focal parakeratosis, focal spongiosis at the follicular opening plus a perifollicular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate. Many of the dermal blood vessels are dilated. In some cases the lymphohistiocytic infiltrate may form granulomas that may be caseating. The granulomas in acne are suppurative due to follicular rupture and reaction to the inflamatory secreted follicular contents into the dermis.
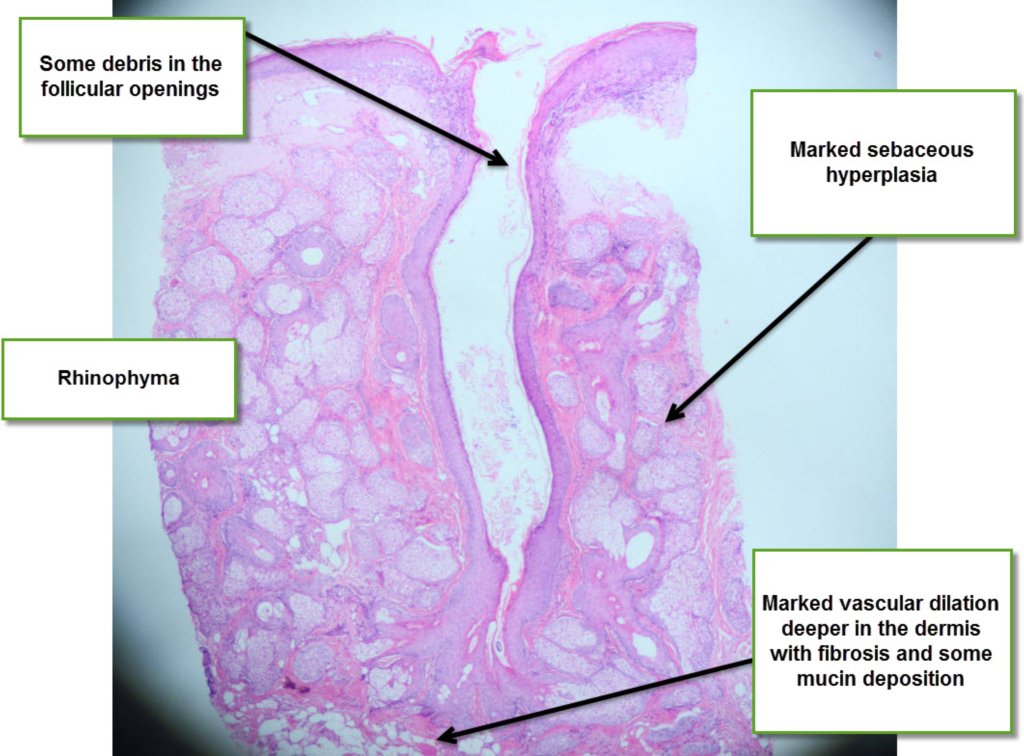
In Rhinophyma there is marked sebaceous hyperplasia and follicular pugging with debris. There also may be marked vascular dilatation with dermal fibrosis and mucin. In cases where these latter features are seen the degree of sebaceous hyperplasia may be minimal!There is a perivascular infiltrate of lymphocytes and plasma cells.
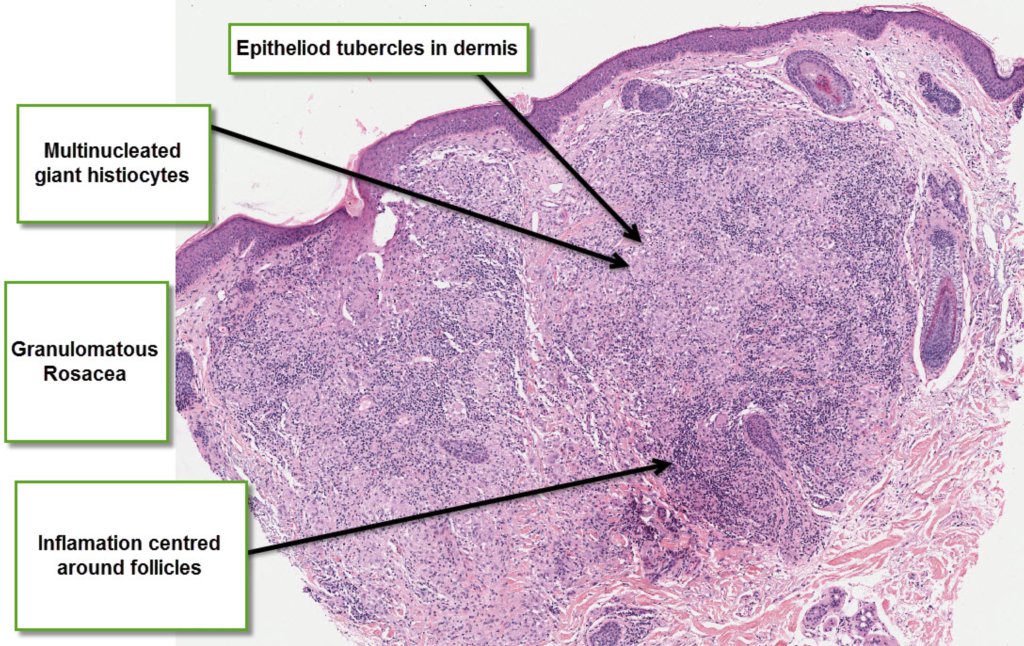
The granulomas in granulomatous rosacea are situated around the hair follicles. They are tuberculoid in nature. About 20% of them may show caseation necrosis.
Papular Rosacea may show features of granulomas, but they are usually associated with the follicles. They can be sarcoidal or naked granulomas or tuberculoid often with lymphocytic infiltrate.
True granulomatous rosacea can resemble lupus vulgaris, caseous necrosis can be seen in rosacea, but it is a more prominent feature of lupus miliaris disseminatus faciei.